
Lets talk about
The Sustainable Development Goals of the United Nations
The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development adopted by all United Nations Member States in 2015, provides a shared blueprint for peace and prosperity for people and the planet, now and into the future.
Panama Sustainability

The UN is the Largest Existing International Organization
We have much to do, in terms of susatinability, in Panama...

The Sustainable Development Goals of the United Nations
Moving Panama forwards towards the sustainable development goals 2030
General Information of the UN´s SDGs

No Poverty
- The decline of global extreme poverty continues, but has slowed. The deceleration indicates that the world is not on track to achieve the target of less than 3 % of the world living in extreme poverty by 2030.
- People who continue to live in extreme poverty face deep, entrenched deprivation often exacerbated by violent conflicts and vulnerability to disasters.
- Strong social protection systems and government spending on key services often help those left behind get back on their feet and escape poverty, but these services need to be brought to scale.

Zero Hunger
- Hunger is on the rise again globally and under nutrition continues to affect millions of children.
- Public investment in agriculture globally is declining, small scale food producers and family farmers require much greater support and increased investment in infrastructure and technology for sustainable agriculture is urgently needed.

Good Health and Well-Being
- Major progress has been made in improving the health of millions of people, increasing life expectancy, reducing maternal and child mortality and fighting against leading communicable diseases.
- However, progress has stalled or is not happening fast enough with regard to addressing major diseases, such as malaria and tuberculosis, while at least half the global population does not have access to essential health services and many of those who do suffer undue financial hardship, potentially pushing them into extreme poverty.
- Concerted efforts are required to achieve universal health coverage and sustainable financing for health, to address the growing burden of non-communicable diseases, including mental health, and to tackle antimicrobial resistance and determinants of health such as air pollution and inadequate water and sanitation.

Quality Education
- Despite the considerable progress on education access and participation over the past years, 262 million children and youth aged 6 to 17 were still out of school in 2017, and more than half of children and adolescents are not meeting minimum proficiency standards in reading and mathematics.
- Rapid technological changes present opportunities and challenges, but the learning environment, the capacities of teachers and the quality of education have not kept pace. Refocused efforts are needed to improve learning outcomes for the full life cycle, especially for women, girls and marginalized people in vulnerable settings.

Gender Equality
While some indicators of gender equality are progressing, such as a significant decline in the prevalence of female genital mutilation and early marriage, the overall numbers continue to be high.
Moreover, insufficient progress on structural issues at the root of gender inequality, such as legal discrimination, unfair social norms and attitudes, decision-making on sexual and reproductive issues and low levels of political participation, are undermining the ability to achieve Sustainable Development Goal 5.

Clean Water and Sanitation
- Despite progress, billions of people still lack safe water, sanitation and handwashing facilities. Data suggests that achieving universal access to even basic sanitation service by 2030 would require doubling the current annual rate of progress¡.
- More efficient use and management of water are critical to addressing the growing demand for water, threats to water security and the increasing frequency and severity of droughts and floods resulting from climate change. As of the time of writing, most countries are unlikely to reach full implementation of integrated water resources¡ management by 2030.

Affordable and Clean Energy
- Access to electricity in the poorest countries has begun to accelerate, energy efficiency continues to improve and renewable energy is making gains in electricity sector.
- Despite this progress, some 800 million people remain without electricity while access to clean cooking fuels and technologies needs dedicated attention. In addition, if Sustainable Development Goals 7, 13 and related Goals are to be met, much higher levels of ambition are required with regard to renewable energy, including transportation and heating.

Decent Work and Economic Growth
- Inclusive and sustainable economic growth can drive progress and generate the means to implement the Sustainable Development Goals. Globally, labour productivity has increased and unemployment is back to prefinancial crisis levels.
- However, the global economy is growing at a slower rate. More progress is needed to increase employment opportunities, particularly for young people, reduce informal employment and the gender pay gap and promote safe and secure working environments to create decent work for all.

Industry, Innovation, Infrastructure
- Aspects of the prevailing global economic environment have not been conducive to rapid progress on Sustainable Development Goal 9.
- While financing for economic infrastructure has increased in developing countries and impressive progress has been made in mobile connectivity, countries that are lagging behind, such as least developed countries, face serious challenges in doubling the manufacturing industry’s share of GDP by 2030, and investment in scientific research and innovation remains below the global average.

Reduced Inequalities
- Inequality within and among nations continues to be a significant concern despite progress in and efforts at narrowing disparities of opportunity, income and¡ power. Income inequality continues to rise in many parts of the world, even as the bottom 40 per cent of the population in many countries has experienced positive growth rates.
- Greater emphasis will need to be placed on reducing inequalities in income as well as those based on other factors. Additional efforts are needed to increase zero-tariff access for exports from least developed countries and developing countries, and assistance to least developed countries and small island developing States.

Sustainable Cities and Communities
- Substantial progress has been made in reducing the proportion of the global urban population living in slums, though more than 1 billion people continue to live in such situations.
- Urgent action is needed to reverse the current situation, which sees the vast majority of urban residents breathing poor-quality air and having limited access to transport and open public spaces. With the areas occupied by cities growing faster than their populations, there are profound repercussions for sustainability.

Responsible Consumption and Production
- Worldwide material consumption has expanded rapidly, as has material footprint per capita, seriously jeopardizing the achievement of Sustainable Development Goal 12 and the Goals more broadly.
- Urgent action is needed to ensure that current material needs do not lead to the overextraction of resources or to the degradation of environmental resources, and should include policies that improve resource efficiency, reduce waste and mainstream sustainability practices across all sectors of the economy.

Climate Action
- With rising greenhouse gas emissions, climate change is occurring at rates much faster than anticipated and its effects are clearly felt worldwide. While there are positive steps in terms of the climate finance flows and the development of nationally determined contributions, far more ambitious plans and accelerated action are needed on mitigation and adaptation.
- Access to finance and strengthened capacities need to be scaled up at a much faster rate, particularly for least developed countries and small island developing States.

Life Below Water
- The expansion of protected areas for marine biodiversity and existing policies and treaties that encourage responsible use of ocean resources are still insufficient to combat the adverse effects of overfishing, growing ocean acidification due to climate change and worsening coastal eutrophication.
- As billions of people depend on oceans for their livelihood and food source and on the transboundary nature of oceans, increased efforts and interventions are needed to conserve and sustainably use ocean resources at all levels.

Life on Land
- There are some encouraging global trends in protecting terrestrial ecosystems and biodiversity. Forest loss is slowing down, more key biodiversity areas are protected and more financial assistance is flowing towards biodiversity protection.
- Yet, the 2020 targets of Sustainable Development Goal 15 are unlikely to be met, land degradation continues, biodiversity loss is occurring at an alarming rate, and invasive species and the illicit poaching and trafficking of wildlife continue to thwart efforts to protect and restore vital ecosystems and species.

Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions
- Advances in ending violence, promoting the rule of law, strengthening institutions and increasing access to justice are uneven and continue to deprive millions of their security, rights and opportunities and undermine the delivery of public services and broader economic development.
- Attacks on civil society are also holding back development progress. Renewed efforts are essential to move towards the achievement of Sustainable Development Goal 16.

Partnership for the Goals
- Progress on some means of implementation targets is moving rapidly: personal remittances are at an all-time high, an increasing proportion of the global population has access to the Internet and the Technology Bank for the Least Developed Countries has been established.
- Yet, significant challenges remain: ODA is declining, private investment flows are not well aligned with sustainable development, there continues to be a significant digital divide and there are ongoing trade tensions. Enhanced international cooperation is needed to ensure that sufficient means of implementation exist to provide countries the opportunity to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals.
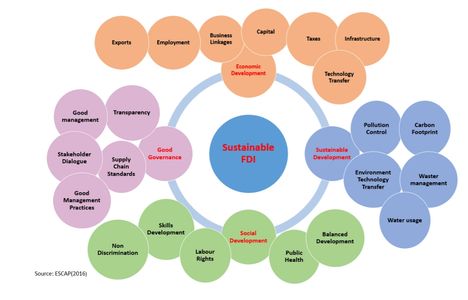
Sustainable Development and the Role of FDI

Private Investment Required to Achieve 2030 Agenda
The success of the SDGs depends on the required level of investment which is estimated to be between US$5 to US$7 trillion per year. Of this, about US$3.3 to US$4.5 trillion is in just the developing countries largely for infrastructure projects such as :
- roads,
- rail networks,
- ports,
- power stations both conventional and renewable energy,
- water and sanitation,
- health,
- education
- and agriculture.
Governance and Regulation
If the SDGs are to be achieved by 2030 then private sector investment in sustainable projects needs to become more significant. This also raises sensitivities as many of the SDGs areas are related to public service. Therefore, governments need to find the fine balance between attracting private sector investment in SDG related projects while protecting public interests through effective governance systems and regulation.
UNCTAD Strategic Framework
Private Sector Investment in SDG
Strategic Framework for Private Investment in the SDGs
Strategic Framework for Private Investment in the SDGs

UNCTAD proposes a Strategic Framework for private sector investment in sustainable projects while seeking to deal with the main policy challenges and options related to the following:
Strategic Framework for Private Investment in the SDGs
Strategic Framework for Private Investment in the SDGs
Strategic Framework for Private Investment in the SDGs

Structure and Components of UNCTAD’s Investment Policy Framework
Structure and Components of UNCTAD’s Investment Policy Framework
Structure and Components of UNCTAD’s Investment Policy Framework

The IPFSD suggests that in assessing an inward investment the following measures can be used:
- Economic value added.
- Value added.
- Contribution to gross fixed capital formation. ◼ Export generation.
- Total fiscal revenues.
- Job creation.
- Number of jobs created (directly and indirectly).
- Wages—household income generated.
- Types of jobs generated.
- Sustainable development.
- Labor impact especially of the economically disadvantaged groups.
- Social impact especially the number of families lifted out of poverty.
- Environmental impact in particular GHG emissions, energy and water consumption, treatment of hazardous materials, enterprise development in ecosectors etc.
- Development impact and technology dissemination.
Assessing Sustainable FDI
Structure and Components of UNCTAD’s Investment Policy Framework
Structure and Components of UNCTAD’s Investment Policy Framework

So, what does the UN do?
The United Nation´s functions:
The UN Charter sets out these main purposes:
- Maintaining worldwide peace and security.
- Developing relations among nations.
- Fostering cooperation between nations in order to solve economic, social, cultural, or humanitarian international problems.

Global Report on Human Development



My Travels
Food and Agriculture Organization
The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger.
Specialized Agencies of the United Nations

Food and Agriculture Organization
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger and improve nutrition and food security. Its Latin motto, fiat panis, translates to "let there be bread".

United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO: is a specialized organization of the United Nations (UN) aimed at contributing "to the building of peace, the eradication of poverty, sustainable development and intercultural dialogue through education, the sciences, culture, communication and information

World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution, which establishes the agency's governing structure and principles, states its main objective as ensuring "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of health."

International Atomic Energy Agency
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) is an international organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy, and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, includingnuclear weapons.

World Meteorological Organization
- Disaster risk reduction
- The Global Framework for Climate Services (GFCS)
- The WMO Integrated Global Observing System (WIGOS)
- Aviation meteorological services
- Polar and high mountain regions
- Capacity development
- Governance

International Labour Organization
The ILO's international labour standards are broadly aimed at ensuring accessible, productive, and sustainable work worldwide in conditions of freedom, equity, security and dignity.

International Civil Aviation Organization
It changes the principles and techniques of international air navigation and fosters the planning and development of international air transport to ensure safe and orderly growth. Its headquarters is located in the Quartier International of Montreal, Quebec Canada.

International Maritime Organization
The IMO's primary purpose is to develop and maintain a comprehensive regulatory framework for shipping and its remit today includes safety, environmental concerns, legal matters, technical co-operation, maritime security and the efficiency of shipping.

Universal Postal Union
UPU is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) that coordinates postal policies among member nations, in addition to the worldwide postal system. The UPU contains four bodies consisting of the Congress, the Council of Administration (CA), the Postal Operations Council (POC) and the International Bureau (IB). It also oversees the Telematics and Express Mail Service (EMS) cooperatives. Each member agrees to the same terms for conducting international postal duties. The UPU's headquarters are located in Bern, Switzerland.

International Development Association
The International Development Association (IDA) (French: Association internationale de développement) is an international financial institution which offers concessional loans and grants to the world's poorest developing countries. The IDA is a member of the World Bank Group and is headquartered in Washington, D.C. in the United States.

World Tourism Organization
The World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) is the United Nations specialized agency responsible for the promotion of responsible, sustainable and universally accessible tourism. It is the leading international organization in the field of tourism, which promotes tourism as a driver of economic growth, inclusive development and environmental sustainability and offers leadership and support to the sector in advancing knowledge and tourism policies worldwide.
My Certifications

University of London
Global Diplomacy: the United Nations in the World

University of Copenhagen
The Sustainable Development Goals: A Global Vision for the Future

Universidad Nacional Autonoma de Mexico
Food Security

University of Copenhagen
Sustainable Tourism: Promoting Environmental Public Health
Contact
Cookie Policy
This website uses cookies. By continuing to use this site, you accept our use of cookies.






